Posterior Tibial Tendonitis/Disfunction Condition
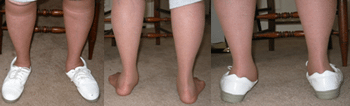
This being said, when the foot pronates excessively the post, the tendon is stressed and placed on a stretch. Excessive pronation must be controlled. Post. Tib. Tednonitis can lead to PTTD (Posterior Tibial Tendon dysfunction) and in advanced cases a Posterior Tibial Tendon Rupture. In these advanced cases foot orthotic therapy is much more aggressive. In the most severe cases an Arizona A.F.O. (Ankle Foot Orthosis) may be used. An A.F.O. uses the lower leg as leverage to stabilize the mid foot, taking the place of the Posterior Tibial Tendon. In older patients, posterior tibial tendonitis is caused by degeneration of the tendon and is less responsive to conservative treatment. A custom calf stretching and strengthening of the posterior tibialis are often prescribed with tendonitis. Physical therapy may be beneficial. Surgery is often used as a last resort.
